Introduction:
Enabling a real-time functionality is one of the real challenges for developers. The developer community has come a long way from HTTP polling to AJAX and has finally come up a solution for building a truly real-time app.
This solution comes in the form of Websockets, which makes it possible for developers to open up an interactive session between a user's browser and a server. Websockets allows to send and receive messages to a server, making a server to generate event-driven responses without having to poll the server for reply.
Nowadays, Websockets are one of the best solution for creating real-time applications, such as multiplayer online games, instant messengers, tracking apps etc. WebSockets are a communications protocol that use full-duplex communication channels over a single durable Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) connection.
With full-duplex communication, both the server and the client can transmit and receive data simultaneously without being blocked, reducing overhead in comparison to alternatives that use half-duplex communication like HTTP polling.

With less overhead, WebSockets enable real-time communication and rapid data transferring between the web server and the web browser or client application. WebSocket communication initiates a handshake, which uses the HTTP Upgrade() header to change from the HTTP protocol to the WebSocket protocol.
Data can be transferred from the server without a prior request from the client, allowing messages to be passed back and forth and keeping the connection open until the client or server kills it. Thus, a two-way real-time data transfer can take place between the client and the server. WebSocket communications are usually done via TCP port number 443.
Building an app using Websockets
In this section, we will be implementing a basic messaging server in Golang
Setting up the HTTP server
Since websockets are built on top of HTTP, our first step would be creating a basic HTTP server that can accept client connections and serve messages. Below is basic http based server written in Golang using library github.com/go-chi/chi
func main() {
router := chi.NewRouter()
router.Route("/", func(ws chi.Router) {
ws.Get("/ws", Websockets)
})
http.ListenAndServe(":8080", nil)
}
Initiating a handshake
To set up a WebSocket connection, a one-time handshake is required between the client and the server. A handshake uses the Upgrade() method to upgrade the HTTP server connection to the WebSocket protocol.
Golang provides multiple libraries like gorilla/websockets (high level, little complexity), gobwas/ws (low level, higher complexity), epoll + gobwas`` if you want to trade even more complexity for significant resource savings.
For the sake of simplicity, we will be usinggithub.com/gorilla/websocket```
Below is the function implementation for Upgrade() for library github.com/gorilla/websocket
conn, err := upgrader.Upgrade(w, r, nil)
if err != nil {
log.Print("upgrade failed: ", err)
return
}
defer conn.Close()
Sending and receiving message using websockets
Below is the handler used for receiving and sending message to the user. The Upgrade function upgrades the HTTP connection to a websocket connection. Within the loop ReadMessage() function accepts messages and WriteMessage() sends the message to the connection.
func Websockets(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
conn, err := upgrades.Upgrade(w, r, nil)
if err != nil {
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusInternalServerError)
return
}
defer conn.Close()
for {
_, body, err := conn.ReadMessage()
if err != nil {
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusInternalServerError)
return
}
fmt.Printf("Recieved: %v", string(body))
if err := conn.WriteMessage(1, []byte("Server Received the message ")); err != nil {
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusInternalServerError)
return
}
}
}
Below is the output from the postman:
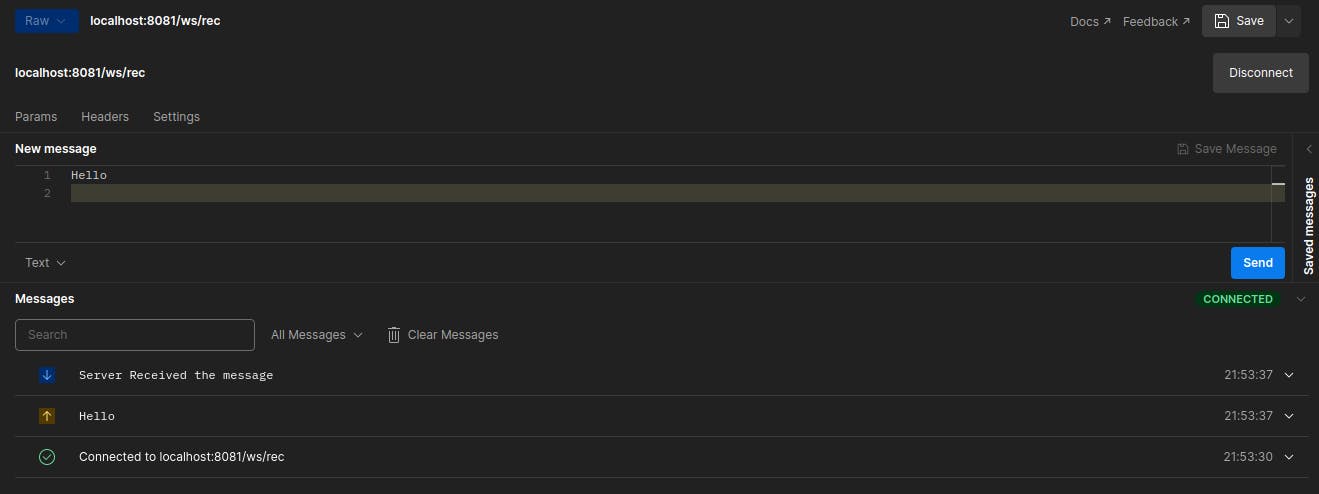
Websockets and Pub-Sub
Most of the novice developers, often gets confused between these two concept. Although both of these concepts are often used when we are taking about server-server or server-client communications, they couldn't be more different. WebSockets as a transportation method, like a plane. It solves the problem of getting the client and server to talk in real-time (e.g. chat applications, notifications, etc). There are other methods like long-short polling (bus), or server-sent events (train). PubSub is a design pattern on how pieces of a system communicate. It's like the subway/airplane system (think JetBlue, Delta Airlines, NYC Subway System, etc). Common tools to handle PubSub today are Kafka and Redis. Some Backend engineers can build an entire career out of designing well-architected, reliable PubSub systems. It can be a very difficult problem.
The concept of Pub-Sub over websockets connections is recently been popularized. The application of the Publish/Subscribe pattern on WebSocket connections resolved the issue of lost messages on WebSocket connections. The framework performances were compared to WebSocket connections itself with regards to messages loss, response latency times, and bandwidth network out. The resulting architecture gives lower latency and message loss.
Applications of Websockets
WebSockets’ primary purpose is to support full-duplex, or two-way communication. Currently, WebSockets offers cross-platform support for Android, iOS, web, and desktop applications, and WebSockets are commonly used in the following types of applications:
- Real-time messaging
- Multiplayer gaming
- Live score feeds
- Collaborative editing tools
- Live location and direction apps
- Audio and video chat using WebRTC
Conclusion
In this blog, we explored Websockets with its brief introduction and their working. To get the better understanding of how websockets work in golang we have implemented a simple messaging app to send and receive data between server and user browser. For our next blog, we will be implementing a chatting service using websockets.

